Research in Health Science (RHS) is an international, double-blind peer-reviewed, open-access journal which is published by Scholink. The journal aims to promote excellence through dissemination of high-quality research findings, specialist knowledge, and discussion of professional issues that reflect the diversity of this field. We would welcome scholars and researchers engaging in the related field to submit your manuscripts which are complete unpublished and original works and not under review in any other journals to Research in Health Science. Both of online submission and E-mail submission (rhs@scholink.org) are acceptable. The scopes of the journal include the following topics:
The journal is included in:
| Open access: Research in Health Science is available online to the reader "without financial, legal, or technical barriers other than those inseparable from gaining access to the internet itself". Peer review: Research in Health Science takes peer review policy. Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people of similar competence to the producers of the work (peers).
|
Journal Publishing Flowchart
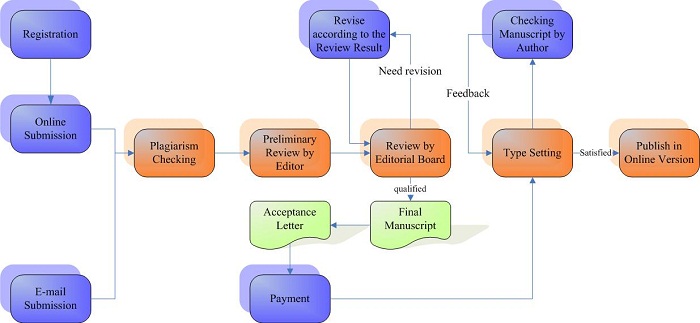
Announcements
Call for Papers for Vol. 11, No. 1, March 2026 |
|
We are calling for submission of papers for Vol. 11, No. 1, March 2026. Submission deadline: February 15th. All submitted articles should be original and must not be under consideration for publication elsewhere. Please submit your manuscripts online. You may also e-mail submissions to rhs@scholink.org |
|
| Posted: 2025-12-08 | |
| More Announcements... |
Vol 11, No 1 (2026)
Table of Contents
Articles
|
Shervin Assari, Hamid Chalian, Mohsen Bazargan
|
p1
|
|
Grace Herrick, Kelly Frasier, Erin Lowe
|
p14
|
|
Jianchen Lin
|
p31
|