World Journal of Education and Humanities (WJEH) is an international, Refereed, double-blind peer-reviewed, open-access journal published by Scholink. The journal aims to provide a high-level platform for scholars and researchers all over the world to share latest findings and views in the field of World Journal of Education and Humanities. We would welcome scholars and researchers engaging in the related field to submit your manuscripts to WJEH. Both of online submission and E-mail submission (wjeh@scholink.org) are acceptable. ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The journal includes, but is not limited to the following fields:
Refereed Journal: World Journal of Education and Humanities is a Refereed Journal Open access: World Journal of Education and Humanities is available online to the reader "without financial, legal, or technical barriers other than those inseparable from gaining access to the internet itself." Peer review: World Journal of Education and Humanities takes peer review policy. Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people of similar competence to the producers of the work (peers). | |
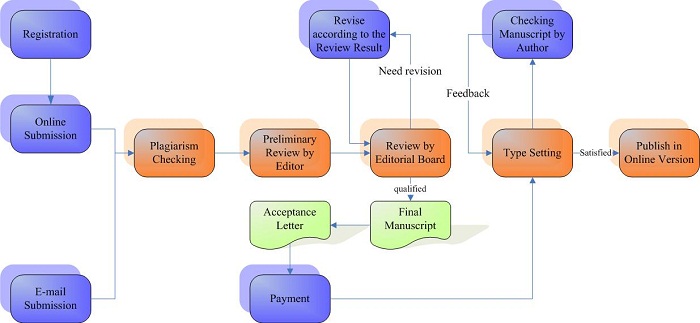
Announcements
Call for Original Papers-Vol 8, No 1, March 2026 |
|
| We are calling for submission of papers for Vol. 8, No. 1, March 2025 (Deadline: March 25, 2026). Please submit your manuscripts online. You may also e-mail submissions to wjeh@scholink.org. If you are interested to be a reviewer, we welcome you to join us. Please download and finish the application form at http://www.scholink.org/doc/Application%20Form%20for%20Editorial%20Board%20Members.doc Then send the completed application form to the editor: wjeh@scholink.org Please pay attention to the basic requirement to reviewer: 1. Possess a doctorial degree. 2. Research area is relative to the subject of journal. 3. Proficiency in English We also would like to cooperate with other institutions to publish special issues. To publish a special issue, please contact with the editor wjeh@scholink.org |
|
| Posted: 2019-06-06 | |
| More Announcements... |
Vol 7, No 6 (2025)
Table of Contents
Articles
|
Gao Li, Bo Tao
|
p1
|
|
JiaXin He, Tingting Zhang, Xiaoyan Hou, Huitong Liao
|
p14
|
|
Yuege Lai, Meiling Chen, Baiyan Du
|
p26
|
|
Xiaohui He, Yewen Lei, Ce Li
|
p34
|
|
Jia Luo
|
p42
|
|
Miyu Ai, Hongxian Chen
|
p51
|
|
Xiaojie Li, Yueling Wu
|
p60
|